You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Human Metabolome Database.
| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:14:58 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000574 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | L-Cysteine |
|---|
| Description | Cysteine (Cys), also known as L-cysteine is an alpha-amino acid. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (-NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. L-alanine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the amino acids used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Cysteine is found in all organisms ranging from bacteria to plants to animals. It is classified as an aliphatic, non-polar, sulfur-containing amino acid. Cysteine is an important source of sulfur in human metabolism, and although it is classified as a non-essential amino acid, cysteine may be essential for infants, the elderly, and individuals with certain metabolic disease or who suffer from malabsorption syndromes. Cysteine can occasionally be considered as an essential or conditionally essential amino acid. Cysteine is unique amongst the twenty natural amino acids as it contains a thiol group. Thiol groups can undergo oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions; when cysteine is oxidized it can form cystine, which is two cysteine residues joined by a disulfide bond. This reaction is reversible since the reduction of this disulphide bond regenerates two cysteine molecules. The disulphide bonds of cystine are crucial to defining the structures of many proteins. Cysteine is often involved in electron-transfer reactions, and help the enzyme catalyze its reaction. Cysteine is also part of the antioxidant glutathione. N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is a form of cysteine where an acetyl group is attached to cysteine's nitrogen atom and is sold as a dietary supplement. Cysteine is named after cystine, which comes from the Greek word kustis meaning bladder (cystine was first isolated from kidney stones). Oxidation of cysteine can produce a disulfide bond with another thiol and further oxidation can produce sulphfinic or sulfonic acids. The cysteine thiol group is also a nucleophile and can undergo addition and substitution reactions. Thiol groups become much more reactive when they are ionized, and cysteine residues in proteins have pKa values close to neutrality, so they are often in their reactive thiolate form in the cell. The thiol group also has a high affinity for heavy metals and proteins containing cysteine will bind metals such as mercury, lead, and cadmium tightly. Due to this ability to undergo redox reactions, cysteine has antioxidant properties. Cysteine is important in energy metabolism. As cystine, it is a structural component of many tissues and hormones. Cysteine has clinical uses ranging from treating baldness to psoriasis to preventing smoker's hack. In some cases, oral cysteine therapy has proved excellent for treatment of asthmatics, enabling them to stop theophylline and other medications. Cysteine also enhances the effect of topically applied silver, tin, and zinc salts in preventing dental cavities. In the future, cysteine may play a role in the treatment of cobalt toxicity, diabetes, psychosis, cancer, and seizures (http://www.dcnutrition.com/AminoAcids/). Cysteine has been identified as a uremic toxin according to the European Uremic Toxin Working Group (PMID: 22626821 ). |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2S/c4-2(1-7)3(5)6/h2,7H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | ChEBI | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid | ChEBI | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | ChEBI | | C | ChEBI | | Cys | ChEBI | | CYSTEINE | ChEBI | | e 920 | ChEBI | | e-920 | ChEBI | | e920 | ChEBI | | FREE cysteine | ChEBI | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid | ChEBI | | L-Cystein | ChEBI | | L-Zystein | ChEBI | | Ecolan | Kegg | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulfanylpropanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulphanylpropanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulphanylpropanoic acid | Generator | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | Generator | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionate | Generator | | (+)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid | HMDB | | (R)-(+)-Cysteine | HMDB | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercapto-propanoate | HMDB | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercapto-propanoic acid | HMDB | | (R)-Cysteine | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionate | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid | HMDB | | 3-Mercapto-L-alanine | HMDB | | Acetylcysteine | HMDB | | alpha-Amino-beta-thiolpropionic acid | HMDB | | b-Mercaptoalanine | HMDB | | beta-Mercaptoalanine | HMDB | | Carbocysteine | HMDB | | Cisteina | HMDB | | Cisteinum | HMDB | | Cystein | HMDB | | Cysteinum | HMDB | | Half-cystine | HMDB | | L Cysteine | HMDB | | L-(+)-Cysteine | HMDB | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | HMDB | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | HMDB | | Polycysteine | HMDB | | Thioserine | HMDB | | Cysteine hydrochloride | HMDB | | Zinc cysteinate | HMDB | | Half cystine | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H7NO2S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 121.158 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 121.019749163 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | L-cysteine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 52-90-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@@H](CS)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2S/c4-2(1-7)3(5)6/h2,7H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cysteine and derivatives. Cysteine and derivatives are compounds containing cysteine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of cysteine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Cysteine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Cysteine or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Amino acid
- Alkylthiol
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 220 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 277 mg/mL at 25 °C | BEILSTEIN | | LogP | -2.49 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| L-Cysteine,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS | 1232.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)SC[C@H](N)C(=O)O | 1396.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O | 1356.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS[Si](C)(C)C | 1430.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS[Si](C)(C)C | 1483.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS[Si](C)(C)C | 1966.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1373.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1346.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1622.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1507.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1480.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1939.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CS)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1542.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CS)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1433.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CS)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1777.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1547.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1544.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1647.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1560.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1545.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1630.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)SC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1674.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)SC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1640.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)SC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1769.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1709.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1691.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1597.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS | 1477.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)SC[C@H](N)C(=O)O | 1634.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O | 1628.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1910.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1945.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2095.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1841.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1804.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1889.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1997.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1935.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2068.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CS)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2011.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CS)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1890.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CS)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1926.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2209.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2208.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2038.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2226.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2211.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1954.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)SC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2354.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)SC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2283.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)SC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2091.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2581.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2504.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | L-Cysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CS[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2105.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (4 TMS) | splash10-00kb-0950000000-df7e91c95b610ff21c79 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (4 TMS) | splash10-00kb-0940000000-aefe34765fb447090a23 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (4 TMS) | splash10-00kb-0970000000-10a155c40ea499023052 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0940000000-037a3a34651c3154b3b3 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (4 TMS) | splash10-00di-9850000000-118c43e33861a6baa8d2 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014j-0690100000-0aeb88fd507505e6b718 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0950000000-df7e91c95b610ff21c79 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0940000000-aefe34765fb447090a23 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0970000000-10a155c40ea499023052 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00kb-0940000000-037a3a34651c3154b3b3 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-QQ (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0uk9-5619100000-8cb2558373966174ced3 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9850000000-118c43e33861a6baa8d2 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0gi0-0960000000-03b2097de6f9637d29cb | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004l-9100000000-4553906a941a5e87ec97 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004i-9200000000-cfaf705cd0452d428454 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-00b9-9600000000-374c5872d68662832769 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-ddbd3df6b8dbb280ffba | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-320a2c77443b80ebf733 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0089-0900000000-9dcd3d757c5cd11eb18e | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-3900000000-212e081fe83ad70de0ad | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-2eb01f41c225f614db24 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-001i-0900000000-a19834eb7cb9f211fdf2 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-2458f2587761e779ed93 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-77e590f0ed26f69b31c0 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-3900000000-7b1857997392b006b95f | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-3900000000-bc268c27ed5706a4bbd2 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine CE-ESI-TOF (CE-system connected to 6210 Time-of-Flight MS, Agilent) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-4573390bccc238e3c91b | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-3900000000-212e081fe83ad70de0ad | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-3900000000-7b1857997392b006b95f | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine QqQ 14V, negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-9000000000-5dc69d3b59bd15290aef | 2020-07-21 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a6r-9100000000-ed3c9c47ed98679090ab | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 0V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-2900000000-8bb219d17ccdf7ac0a5d | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-e623d5a27b5075c82b4d | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-056r-9100000000-4e26cc13af7c878115f7 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00b9-9600000000-4352a7b437c34c04d9f0 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-9200000000-7b4cd034c717561c61dd | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052f-9000000000-8f351cbca6ffed356a9b | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-6900000000-51ba0df80cc33423420b | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0079-9400000000-4aa2b707c391d5838d29 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - L-Cysteine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-9000000000-95c7672c7836c0fc51c9 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2021-10-10 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Mitochondria
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Saliva
- Sweat
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Adrenal Cortex
- Epidermis
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
- Kidney
- Liver
- Neuron
- Placenta
- Platelet
- Prostate
- Skeletal Muscle
- Spleen
- Testis
- Thyroid Gland
|
|---|
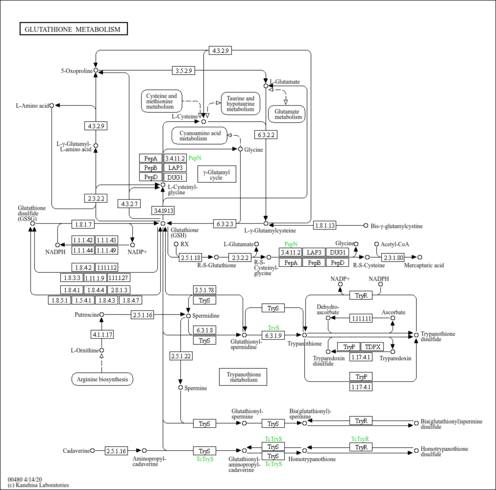
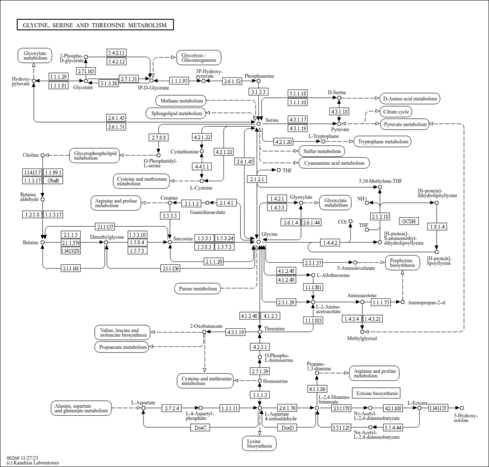
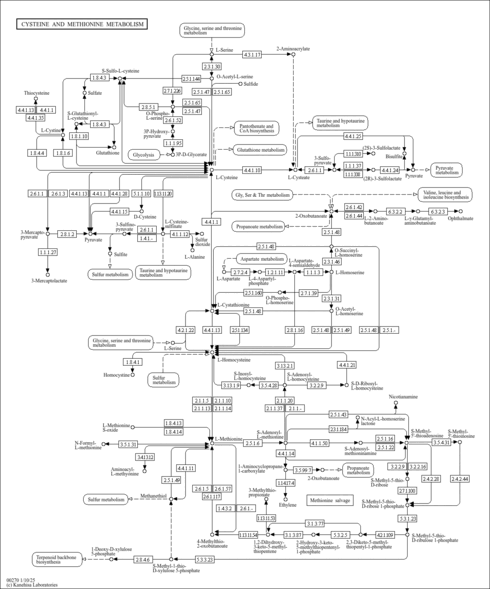
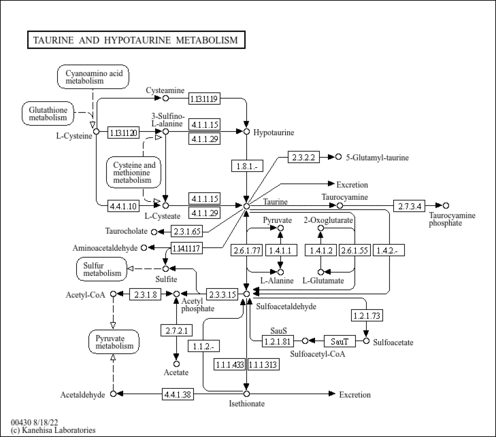
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 24-100 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 197.00 +/- 56.00 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 131.00 +/- 40.00 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 210.00 +/- 40.00 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.36 +/- 0.02 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 212.00 +/- 23.00 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 197.0-283.0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 52.0 (41.0-63.0) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 231.07-307.90 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 33.5 +/- 10.3 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.054 (0.017-0.108) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 1.30 +/- 0.26 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Sweat | Detected and Quantified | < 10 uM | Adult (60 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Sweat | Detected and Quantified | < 10 uM | Adult (40 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 34(26-50) umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.322 (1.447-5.197) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 22-27 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 30.32 +/- 24.58 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 81.0 (36.7-147.6) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 32.00 +/- 10.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 28.00 +/- 9.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 34.4 +/- 11.00 umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 33.4 +/- 15.5 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 19-27 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 65.8 (23.1-134.5) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 22.591 +/- 10.057 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 14.9 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.355 (0.157-1.146) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Multiple sclerosis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.420 (0.154-0.874) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Stroke | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.415 (0.199-1.038) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Peripheral neuropathy | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.491 (0.247-1.764) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Dementia (Alzheimer's and non-Alzheimer's) | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5000000 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Sulfite oxidase deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.56 +/- 0.03 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | uremia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <5 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Sulfite oxidase deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 13.0 (10.0-16.0) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | AIDS | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 12.81 +/- 2.17 uM | Elderly (>65 years old) | Both | Alzheimer's Disease | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.042 (0.022-0.10) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Multiple sclerosis | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.048 (0.018-0.10) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Stroke | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.034 (0.018-0.075) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Peripheral neuropathy | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.047 (0.025-0.125) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Dementia (Alzheimer's and non-Alzheimer's) | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Autism | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 81-106 umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Male | Cystinylglycinuria | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 29.971 +/- 24.6 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | AIDS |
|---|
- Naisbitt DJ, Vilar FJ, Stalford AC, Wilkins EG, Pirmohamed M, Park BK: Plasma cysteine deficiency and decreased reduction of nitrososulfamethoxazole with HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Dec 10;16(18):1929-38. [PubMed:11153075 ]
| | Alzheimer's disease |
|---|
- Fonteh AN, Harrington RJ, Tsai A, Liao P, Harrington MG: Free amino acid and dipeptide changes in the body fluids from Alzheimer's disease subjects. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):213-24. Epub 2006 Oct 10. [PubMed:17031479 ]
| | Uremia |
|---|
- Duranton F, Cohen G, De Smet R, Rodriguez M, Jankowski J, Vanholder R, Argiles A: Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jul;23(7):1258-70. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011121175. Epub 2012 May 24. [PubMed:22626821 ]
| | Sulfite oxidase deficiency, ISOLATED |
|---|
- Rocha S, Ferreira AC, Dias AI, Vieira JP, Sequeira S: Sulfite oxidase deficiency--an unusual late and mild presentation. Brain Dev. 2014 Feb;36(2):176-9. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2013.01.013. Epub 2013 Feb 27. [PubMed:23452914 ]
- Choong T. et al. (2010). Clinical and Laboratory Barriers to the Timely Diagnosis of Sulphite Oxidase Deficiency. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare, 19(2), 94-100.. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare.
| | Multiple sclerosis |
|---|
- Obeid R, Kasoha M, Knapp JP, Kostopoulos P, Becker G, Fassbender K, Herrmann W: Folate and methylation status in relation to phosphorylated tau protein(181P) and beta-amyloid(1-42) in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007 Jun;53(6):1129-36. Epub 2007 Mar 23. [PubMed:17384003 ]
| | Stroke |
|---|
- Obeid R, Kasoha M, Knapp JP, Kostopoulos P, Becker G, Fassbender K, Herrmann W: Folate and methylation status in relation to phosphorylated tau protein(181P) and beta-amyloid(1-42) in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007 Jun;53(6):1129-36. Epub 2007 Mar 23. [PubMed:17384003 ]
| | Peripheral neuropathy |
|---|
- Obeid R, Kasoha M, Knapp JP, Kostopoulos P, Becker G, Fassbender K, Herrmann W: Folate and methylation status in relation to phosphorylated tau protein(181P) and beta-amyloid(1-42) in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007 Jun;53(6):1129-36. Epub 2007 Mar 23. [PubMed:17384003 ]
| | Dementia |
|---|
- Obeid R, Kasoha M, Knapp JP, Kostopoulos P, Becker G, Fassbender K, Herrmann W: Folate and methylation status in relation to phosphorylated tau protein(181P) and beta-amyloid(1-42) in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007 Jun;53(6):1129-36. Epub 2007 Mar 23. [PubMed:17384003 ]
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Monleon D, Morales JM, Barrasa A, Lopez JA, Vazquez C, Celda B: Metabolite profiling of fecal water extracts from human colorectal cancer. NMR Biomed. 2009 Apr;22(3):342-8. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1345. [PubMed:19006102 ]
- Ni Y, Xie G, Jia W: Metabonomics of human colorectal cancer: new approaches for early diagnosis and biomarker discovery. J Proteome Res. 2014 Sep 5;13(9):3857-70. doi: 10.1021/pr500443c. Epub 2014 Aug 14. [PubMed:25105552 ]
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Autism |
|---|
- De Angelis M, Piccolo M, Vannini L, Siragusa S, De Giacomo A, Serrazzanetti DI, Cristofori F, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R: Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 9;8(10):e76993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076993. eCollection 2013. [PubMed:24130822 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
| | Cystinylglycinuria |
|---|
- Bellet H, Rejou F, Vallat C, Mion H, Dimeglio A: Cystinylglycinuria: a new neurometabolic disorder? J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999 May;22(3):231-4. [PubMed:10384375 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00151 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB012678 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001351 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 5653 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00097 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CYS |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33843 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Cysteine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 5556 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5862 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17561 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | CYS_L |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000192 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Kumagai, Hidehiko; Tanaka, Hideyuki; Sejima, Shunsuke; Yamada, Hideaki. Elimination and replacement reactions of b-chloro-L-alanine by cysteine desulfhydrase from Aerobacter aerogenes. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry (1977), 41(10), 2071-5. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Yu FH, Westenbroek RE, Silos-Santiago I, McCormick KA, Lawson D, Ge P, Ferriera H, Lilly J, DiStefano PS, Catterall WA, Scheuer T, Curtis R: Sodium channel beta4, a new disulfide-linked auxiliary subunit with similarity to beta2. J Neurosci. 2003 Aug 20;23(20):7577-85. [PubMed:12930796 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Nicholson JK, O'Flynn MP, Sadler PJ, Macleod AF, Juul SM, Sonksen PH: Proton-nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of serum, plasma and urine from fasting normal and diabetic subjects. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):365-75. [PubMed:6696735 ]
- Cynober LA: Plasma amino acid levels with a note on membrane transport: characteristics, regulation, and metabolic significance. Nutrition. 2002 Sep;18(9):761-6. [PubMed:12297216 ]
- Kersemans V, Cornelissen B, Kersemans K, Bauwens M, Achten E, Dierckx RA, Mertens J, Slegers G: In vivo characterization of 123/125I-2-iodo-L-phenylalanine in an R1M rhabdomyosarcoma athymic mouse model as a potential tumor tracer for SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2005 Mar;46(3):532-9. [PubMed:15750170 ]
- Sandmann J, Schwedhelm KS, Tsikas D: Specific transport of S-nitrosocysteine in human red blood cells: Implications for formation of S-nitrosothiols and transport of NO bioactivity within the vasculature. FEBS Lett. 2005 Aug 1;579(19):4119-24. [PubMed:16023102 ]
- Paivalainen S, Suokas M, Lahti O, Heape AM: Degraded myelin-associated glycoprotein (dMAG) formation from pure human brain myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) is not mediated by calpain or cathepsin L-like activities. J Neurochem. 2003 Feb;84(3):533-45. [PubMed:12558973 ]
- Iyer S, Leonidas DD, Swaminathan GJ, Maglione D, Battisti M, Tucci M, Persico MG, Acharya KR: The crystal structure of human placenta growth factor-1 (PlGF-1), an angiogenic protein, at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 13;276(15):12153-61. Epub 2000 Nov 7. [PubMed:11069911 ]
- Nishiya Y, Yoshida Y, Yoshimura M, Fukamachi H, Nakano Y: Homogeneous enzymatic assay for L-cysteine with betaC-S lyase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2005 Nov;69(11):2244-6. [PubMed:16306712 ]
- Santamaria I, Velasco G, Cazorla M, Fueyo A, Campo E, Lopez-Otin C: Cathepsin L2, a novel human cysteine proteinase produced by breast and colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998 Apr 15;58(8):1624-30. [PubMed:9563472 ]
- Eriksson A, Tohonen V, Wedell A, Nordqvist K: Isolation of the human testatin gene and analysis in patients with abnormal gonadal development. Mol Hum Reprod. 2002 Jan;8(1):8-15. [PubMed:11756564 ]
- Kaminska J, Wisniewska A, Koscielak J: Chemical modifications of alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase define amino acid residues of catalytic importance. Biochimie. 2003 Mar-Apr;85(3-4):303-10. [PubMed:12770769 ]
- Li Y, Gamper N, Shapiro MS: Single-channel analysis of KCNQ K+ channels reveals the mechanism of augmentation by a cysteine-modifying reagent. J Neurosci. 2004 Jun 2;24(22):5079-90. [PubMed:15175377 ]
- Lindzen M, Gottschalk KE, Fuzesi M, Garty H, Karlish SJ: Structural interactions between FXYD proteins and Na+,K+-ATPase: alpha/beta/FXYD subunit stoichiometry and cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):5947-55. Epub 2005 Dec 21. [PubMed:16373350 ]
- Norris FA, Wilson MP, Wallis TS, Galyov EE, Majerus PW: SopB, a protein required for virulence of Salmonella dublin, is an inositol phosphate phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Nov 24;95(24):14057-9. [PubMed:9826652 ]
- Foss CA, Mease RC, Fan H, Wang Y, Ravert HT, Dannals RF, Olszewski RT, Heston WD, Kozikowski AP, Pomper MG: Radiolabeled small-molecule ligands for prostate-specific membrane antigen: in vivo imaging in experimental models of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 1;11(11):4022-8. [PubMed:15930336 ]
- Kozaki K, Miyaishi O, Asai N, Iida K, Sakata K, Hayashi M, Nishida T, Matsuyama M, Shimizu S, Kaneda T, et al.: Tissue distribution of ERp61 and association of its increased expression with IgG production in hybridoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Aug;213(2):348-58. [PubMed:8050492 ]
- Amberger VR, Hensel T, Ogata N, Schwab ME: Spreading and migration of human glioma and rat C6 cells on central nervous system myelin in vitro is correlated with tumor malignancy and involves a metalloproteolytic activity. Cancer Res. 1998 Jan 1;58(1):149-58. [PubMed:9426071 ]
- Zhang JT, Li QX, Wang D, Zhu ZL, Yang YH, Cui DS, Wang MW, Sun XF: Up-regulation of PINCH in the stroma of oral squamous cell carcinoma predicts nodal metastasis. Oncol Rep. 2005 Dec;14(6):1519-22. [PubMed:16273248 ]
- Taveau M, Bourg N, Sillon G, Roudaut C, Bartoli M, Richard I: Calpain 3 is activated through autolysis within the active site and lyses sarcomeric and sarcolemmal components. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Dec;23(24):9127-35. [PubMed:14645524 ]
- Naisbitt DJ, Vilar FJ, Stalford AC, Wilkins EG, Pirmohamed M, Park BK: Plasma cysteine deficiency and decreased reduction of nitrososulfamethoxazole with HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Dec 10;16(18):1929-38. [PubMed:11153075 ]
- Baker DH, Czarnecki-Maulden GL: Pharmacologic role of cysteine in ameliorating or exacerbating mineral toxicities. J Nutr. 1987 Jun;117(6):1003-10. [PubMed:3298579 ]
- Bulaj G, Kortemme T, Goldenberg DP: Ionization-reactivity relationships for cysteine thiols in polypeptides. Biochemistry. 1998 Jun 23;37(25):8965-72. [PubMed:9636038 ]
- Duranton F, Cohen G, De Smet R, Rodriguez M, Jankowski J, Vanholder R, Argiles A: Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jul;23(7):1258-70. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011121175. Epub 2012 May 24. [PubMed:22626821 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
|
|---|