| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:08 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001072 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Coenzyme Q10 |
|---|
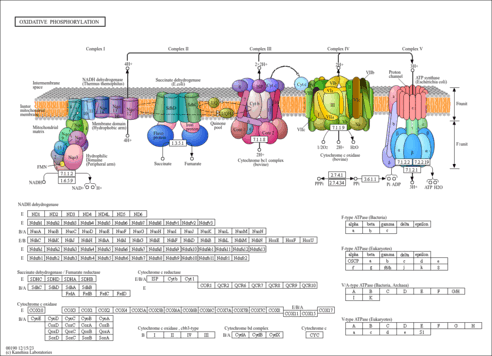
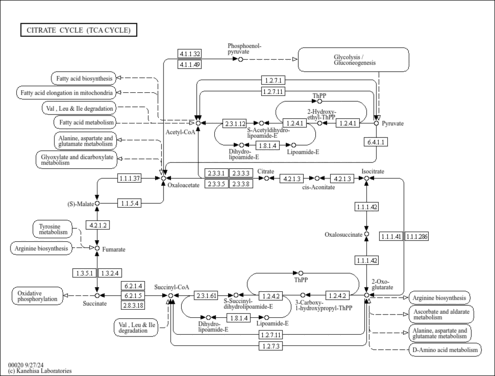
| Description | Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone) is a naturally occurring compound widely distributed in animal organisms and in humans. The primary compounds involved in the biosynthesis of ubiquinone are 4-hydroxybenzoate and the polyprenyl chain. An essential role of coenzyme Q10 is as an electron carrier in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Moreover, coenzyme Q10 is one of the most important lipophilic antioxidants, preventing the generation of free radicals as well as oxidative modifications of proteins, lipids, and DNA, it and can also regenerate the other powerful lipophilic antioxidant, alpha-tocopherol. Antioxidant action is a property of the reduced form of coenzyme Q10, ubiquinol (CoQ10H2), and the ubisemiquinone radical (CoQ10H*). Paradoxically, independently of the known antioxidant properties of coenzyme Q10, the ubisemiquinone radical anion (CoQ10-) possesses prooxidative properties. Decreased levels of coenzyme Q10 in humans are observed in many pathologies (e.g. cardiac disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, AIDS, cancer) associated with intensive generation of free radicals and their action on cells and tissues. In these cases, treatment involves pharmaceutical supplementation or increased consumption of coenzyme Q10 with meals as well as treatment with suitable chemical compounds (i.e. folic acid or B-group vitamins) which significantly increase ubiquinone biosynthesis in the organism. Estimation of coenzyme Q10 deficiency and efficiency of its supplementation requires a determination of ubiquinone levels in the organism. Therefore, highly selective and sensitive methods must be applied, such as HPLC with UV or coulometric detection. For a number of years, coenzyme Q (CoQ10 in humans) was known for its key role in mitochondrial bioenergetics; later studies demonstrated its presence in other subcellular fractions and in plasma, and extensively investigated its antioxidant role. These two functions constitute the basis on which research supporting the clinical use of CoQ10 is founded. Also at the inner mitochondrial membrane level, coenzyme Q is recognized as an obligatory co-factor for the function of uncoupling proteins and a modulator of the transition pore. Furthermore, recent data reveal that CoQ10 affects expression of genes involved in human cell signalling, metabolism, and transport and some of the effects of exogenously administered CoQ10 may be due to this property. Coenzyme Q is the only lipid soluble antioxidant synthesized endogenously. In its reduced form, CoQH2, ubiquinol, inhibits protein and DNA oxidation but it is the effect on lipid peroxidation that has been most deeply studied. Ubiquinol inhibits the peroxidation of cell membrane lipids and also that of lipoprotein lipids present in the circulation. Dietary supplementation with CoQ10 results in increased levels of ubiquinol-10 within circulating lipoproteins and increased resistance of human low-density lipoproteins to the initiation of lipid peroxidation. Moreover, CoQ10 has a direct anti-atherogenic effect, which has been demonstrated in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice fed with a high-fat diet. (PMID: 15928598 , 17914161 ). |
|---|
| Structure | COC1=C(OC)C(=O)C(C\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CCC=C(C)C)=C(C)C1=O InChI=1S/C59H90O4/c1-44(2)24-15-25-45(3)26-16-27-46(4)28-17-29-47(5)30-18-31-48(6)32-19-33-49(7)34-20-35-50(8)36-21-37-51(9)38-22-39-52(10)40-23-41-53(11)42-43-55-54(12)56(60)58(62-13)59(63-14)57(55)61/h24,26,28,30,32,34,36,38,40,42H,15-23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43H2,1-14H3/b45-26+,46-28+,47-30+,48-32+,49-34+,50-36+,51-38+,52-40+,53-42+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2-((all-e)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Decamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecaenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-p-benzoquinone | ChEBI | | 2-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E,34E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Decamethyltetraconta-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-decaen-1-yl]-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone | ChEBI | | Adelir | ChEBI | | all-trans-Ubiquinone | ChEBI | | CoQ | ChEBI | | CoQ10 | ChEBI | | Q | ChEBI | | Q 199 | ChEBI | | Q10 | ChEBI | | Ubidecarenone | ChEBI | | Ubiquinone | ChEBI | | Ubiquinone 10 | ChEBI | | Ubiquinone 50 | ChEBI | | UBIQUINONE-10 | ChEBI | | CoQ 10 | HMDB | | 2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-decaprenylbenzoquinone | HMDB | | Bio-quinone Q10 | HMDB | | Ubiquinone Q10 | HMDB | | Q-Ter | HMDB | | CO-Enzyme Q10 | HMDB | | (all-e)-2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31-octamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30-dotriacontaoctaenyl)-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione | HMDB | | (all-e)-2-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Decamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecaenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione | HMDB | | 2-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Decamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecaenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-p-benzoquinone | HMDB | | 2-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E,34E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Decamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecaenyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl- 2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione | HMDB | | 4-Ethyl-5-fluoropyrimidine | HMDB | | Aqua Q 10l10 | HMDB | | Aqua Q10 | HMDB | | Bio-quinon | HMDB | | Ensorb | HMDB | | Kaneka Q10 | HMDB | | Kudesan | HMDB | | Li-Q-sorb | HMDB | | Liquid-Q | HMDB | | Neuquinon | HMDB | | Neuquinone | HMDB | | PureSorb Q 40 | HMDB | | Q 10AA | HMDB | | Q-Gel | HMDB | | Q-Gel 100 | HMDB | | Unbiquinone | HMDB | | Unispheres Q 10 | HMDB | | Coenzyme Q10 | KEGG |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C59H90O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 863.3435 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 862.683911368 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E,34E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-decamethyltetraconta-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-decaen-1-yl]-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione |
|---|
| Traditional Name | coenzyme-Q10 |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 303-98-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | COC1=C(OC)C(=O)C(C\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CCC=C(C)C)=C(C)C1=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C59H90O4/c1-44(2)24-15-25-45(3)26-16-27-46(4)28-17-29-47(5)30-18-31-48(6)32-19-33-49(7)34-20-35-50(8)36-21-37-51(9)38-22-39-52(10)40-23-41-53(11)42-43-55-54(12)56(60)58(62-13)59(63-14)57(55)61/h24,26,28,30,32,34,36,38,40,42H,15-23,25,27,29,31,33,35,37,39,41,43H2,1-14H3/b45-26+,46-28+,47-30+,48-32+,49-34+,50-36+,51-38+,52-40+,53-42+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | ACTIUHUUMQJHFO-UPTCCGCDSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as ubiquinones. These are coenzyme Q derivatives containing a 5, 6-dimethoxy-3-methyl(1,4-benzoquinone) moiety to which an isoprenyl group is attached at ring position 2(or 6). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Quinone and hydroquinone lipids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Ubiquinones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Polyterpenoid
- Polyprenylbenzoquinone
- Ubiquinone skeleton
- Quinone
- P-benzoquinone
- Vinylogous ester
- Cyclic ketone
- Ketone
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Not Available | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized |
|---|
| MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03dj-0211112090-13e67655f61e48a95d91 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kb-0859598220-67d1d2437197bf4977c9 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014j-1132229710-87eed3c798b1c43399ec | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000000090-68b5c91d1736a6033778 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-08fs-0100000390-3f2c6d6cc684a14c6586 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000b-8100000890-af49da707a25798624ae | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-0000000090-a6d03131917f48e133bd | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0401-0610000090-dc4b3b3f945aad4d4257 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0159-0390020220-89b5a282573b01b279b5 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0lxt-4604144690-1c8a7d6e65a6bdea91f2 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-2904643200-44e3daf814c9cf3545a5 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Coenzyme Q10 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0059-9513721000-094a787c7f6611385e57 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | 2022-08-21 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| General References | - Siciliano G, Mancuso M, Tedeschi D, Manca ML, Renna MR, Lombardi V, Rocchi A, Martelli F, Murri L: Coenzyme Q10, exercise lactate and CTG trinucleotide expansion in myotonic dystrophy. Brain Res Bull. 2001 Oct-Nov 1;56(3-4):405-10. [PubMed:11719279 ]
- Appelkvist EL, Edlund C, Low P, Schedin S, Kalen A, Dallner G: Effects of inhibitors of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase on coenzyme Q and dolichol biosynthesis. Clin Investig. 1993;71(8 Suppl):S97-102. [PubMed:8241713 ]
- Lalani SR, Vladutiu GD, Plunkett K, Lotze TE, Adesina AM, Scaglia F: Isolated mitochondrial myopathy associated with muscle coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Arch Neurol. 2005 Feb;62(2):317-20. [PubMed:15710863 ]
- Mosca L, Marcellini S, Perluigi M, Mastroiacovo P, Moretti S, Famularo G, Peluso I, Santini G, De Simone C: Modulation of apoptosis and improved redox metabolism with the use of a new antioxidant formula. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002 Apr 1;63(7):1305-14. [PubMed:11960607 ]
- Zierz S, von Wersebe O, Bleistein J, Jerusalem F: Exogenous coenzyme Q (coq) fails to increase coq in skeletal muscle of two patients with mitochondrial myopathies. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Mar;95(3):283-90. [PubMed:2358821 ]
- Sekine K, Ota N, Nishii M, Uetake T, Shimadzu M: Estimation of plasma and saliva levels of coenzyme Q10 and influence of oral supplementation. Biofactors. 2005;25(1-4):205-11. [PubMed:16873948 ]
- Zhou S, Zhang Y, Davie A, Marshall-Gradisnik S, Hu H, Wang J, Brushett D: Muscle and plasma coenzyme Q10 concentration, aerobic power and exercise economy of healthy men in response to four weeks of supplementation. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2005 Sep;45(3):337-46. [PubMed:16230985 ]
- Folkers K, Hanioka T, Xia LJ, McRee JT Jr, Langsjoen P: Coenzyme Q10 increases T4/T8 ratios of lymphocytes in ordinary subjects and relevance to patients having the AIDS related complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):786-91. [PubMed:1673841 ]
- Mancini A, De Marinis L, Oradei A, Hallgass ME, Conte G, Pozza D, Littarru GP: Coenzyme Q10 concentrations in normal and pathological human seminal fluid. J Androl. 1994 Nov-Dec;15(6):591-4. [PubMed:7721661 ]
- Hanisch F, Zierz S: Only transient increase of serum CoQ subset 10 during long-term CoQ10 therapy in mitochondrial ophthalmoplegia. Eur J Med Res. 2003 Nov 12;8(11):485-91. [PubMed:14644702 ]
- Ogasahara S, Engel AG, Frens D, Mack D: Muscle coenzyme Q deficiency in familial mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2379-82. [PubMed:2928337 ]
- Ye CQ, Folkers K, Tamagawa H, Pfeiffer C: A modified determination of coenzyme Q10 in human blood and CoQ10 blood levels in diverse patients with allergies. Biofactors. 1988 Dec;1(4):303-6. [PubMed:3255359 ]
- Singh RB, Niaz MA, Rastogi SS, Shukla PK, Thakur AS: Effect of hydrosoluble coenzyme Q10 on blood pressures and insulin resistance in hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease. J Hum Hypertens. 1999 Mar;13(3):203-8. [PubMed:10204818 ]
- Van Maldergem L, Trijbels F, DiMauro S, Sindelar PJ, Musumeci O, Janssen A, Delberghe X, Martin JJ, Gillerot Y: Coenzyme Q-responsive Leigh's encephalopathy in two sisters. Ann Neurol. 2002 Dec;52(6):750-4. [PubMed:12447928 ]
- Tomasetti M, Alleva R, Solenghi MD, Littarru GP: Distribution of antioxidants among blood components and lipoproteins: significance of lipids/CoQ10 ratio as a possible marker of increased risk for atherosclerosis. Biofactors. 1999;9(2-4):231-40. [PubMed:10416035 ]
- Ogasahara S, Yorifuji S, Nishikawa Y, Takahashi M, Wada K, Hazama T, Nakamura Y, Hashimoto S, Kono N, Tarui S: Improvement of abnormal pyruvate metabolism and cardiac conduction defect with coenzyme Q10 in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology. 1985 Mar;35(3):372-7. [PubMed:3974895 ]
- Mancini A, Conte B, De Marinis L, Hallgass ME, Pozza D, Oradei A, Littarru GP: Coenzyme Q10 levels in human seminal fluid: diagnostic and clinical implications. Mol Aspects Med. 1994;15 Suppl:s249-55. [PubMed:7752837 ]
- Zierz S, Jahns G, Jerusalem F: Coenzyme Q in serum and muscle of 5 patients with Kearns-Sayre syndrome and 12 patients with ophthalmoplegia plus. J Neurol. 1989 Feb;236(2):97-101. [PubMed:2709060 ]
- Miyake Y, Shouzu A, Nishikawa M, Yonemoto T, Shimizu H, Omoto S, Hayakawa T, Inada M: Effect of treatment with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on serum coenzyme Q10 in diabetic patients. Arzneimittelforschung. 1999 Apr;49(4):324-9. [PubMed:10337451 ]
- De Luca C, Filosa A, Grandinetti M, Maggio F, Lamba M, Passi S: Blood antioxidant status and urinary levels of catecholamine metabolites in beta-thalassemia. Free Radic Res. 1999 Jun;30(6):453-62. [PubMed:10400457 ]
- Siemieniuk E, Skrzydlewska E: [Coenzyme Q10: its biosynthesis and biological significance in animal organisms and in humans]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2005;59:150-9. [PubMed:15928598 ]
- Littarru GP, Tiano L: Bioenergetic and antioxidant properties of coenzyme Q10: recent developments. Mol Biotechnol. 2007 Sep;37(1):31-7. [PubMed:17914161 ]
|
|---|