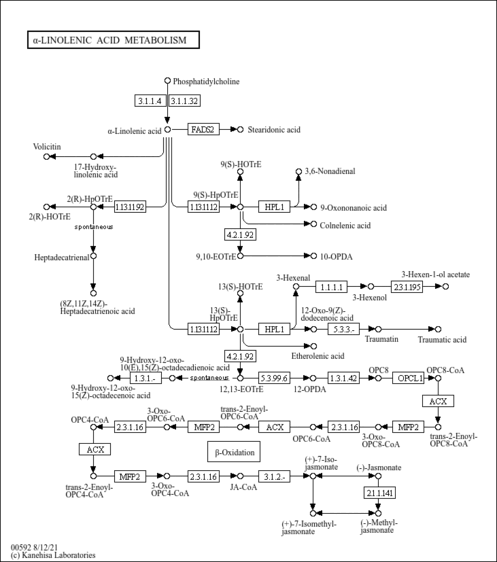
Showing metabocard for Calcium (HMDB0000464)
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 1085 proteins in total.
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Has transacylase and calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity. Catalyzes the formation of 1-O-acyl-N-acetylsphingosine and the concomitant release of a lyso-phospholipid (By similarity). May have weak lysophospholipase activity.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G15
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8NCC3
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- PA2 catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides. This isozyme hydrolyzes more efficiently L-alpha-1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl phosphatidylcholine than L-alpha-1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonyl phosphatidylcholine, L-alpha-1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonyl phosphatidylethanolamine, or L-alpha-1-stearoyl-2-arachidonyl phosphatidylinositol. May be involved in the production of lung surfactant, the remodeling or regulation of cardiac muscle.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G5
- Uniprot ID:
- P39877
- Molecular weight:
- 15674.065
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- PA2 catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides. Hydrolyzes phosphatidylglycerol versus phosphatidylcholine with a 15-fold preference.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G2F
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BZM2
- Molecular weight:
- 23256.29
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Selectively hydrolyzes arachidonyl phospholipids in the sn-2 position releasing arachidonic acid. Together with its lysophospholipid activity, it is implicated in the initiation of the inflammatory response.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P47712
- Molecular weight:
- 85210.19
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- PA2 catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P04054
- Molecular weight:
- 16359.535
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- Not known; does not seem to have catalytic activity.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G12B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BX93
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- PA2 catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides. Has a powerful potency for releasing arachidonic acid from cell membrane phospholipids. Prefers phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine liposomes to those of phosphatidylserine.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G10
- Uniprot ID:
- O15496
- Molecular weight:
- 18153.04
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- PA2 catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides. Has a preference for arachidonic-containing phospholipids.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G2E
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NZK7
- Molecular weight:
- 15988.525
- General function:
- Involved in phospholipase A2 activity
- Specific function:
- PA2 catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides. Does not exhibit detectable activity toward sn-2-arachidonoyl- or linoleoyl-phosphatidylcholine or -phosphatidylethanolamine.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G12A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BZM1
- Molecular weight:
- 21066.99
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the release of fatty acids from phospholipids. It has been implicated in normal phospholipid remodeling, nitric oxide-induced or vasopressin-induced arachidonic acid release and in leukotriene and prostaglandin production. May participate in fas mediated apoptosis and in regulating transmembrane ion flux in glucose-stimulated B-cells. Has a role in cardiolipin (CL) deacylation. Required for both speed and directionality of monocyte MCP1/CCL2-induced chemotaxis through regulation of F-actin polymerization at the pseudopods. Isoform ankyrin-iPLA2-1 and isoform ankyrin-iPLA2-2, which lack the catalytic domain, are probably involved in the negative regulation of iPLA2 activity.
- Gene Name:
- PLA2G6
- Uniprot ID:
- O60733
- Molecular weight:
- 84092.635
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in calcium ion binding
- Specific function:
- Cotransporter which plays a role in lipoprotein, vitamin and iron metabolism, by facilitating their uptake. Binds to ALB, MB, Kappa and lambda-light chains, TF, hemoglobin, GC, SCGB1A1, APOA1, high density lipoprotein, and the GIF-cobalamin complex. The binding of all ligands required calcium. Serves as important transporter in several absorptive epithelia, including intestine, renal proximal tubules and embryonic yolk sac. Interaction with LRP2 mediates its trafficking throughout vesicles and facilitates the uptake of specific ligands like GC, hemoglobin, ALB, TF and SCGB1A1. Interaction with AMN controls its trafficking to the plasma membrane and facilitates endocytosis of ligands. May play an important role in the development of the peri-implantation embryo through internalization of APOA1 and cholesterol. Binds to LGALS3 at the maternal-fetal interface
- Gene Name:
- CUBN
- Uniprot ID:
- O60494
- Molecular weight:
- 398672.8
- General function:
- Involved in ion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in the renal elimination of endogenous and exogenous organic anions. Functions as organic anion exchanger when the uptake of one molecule of organic anion is coupled with an efflux of one molecule of endogenous dicarboxylic acid (glutarate, ketoglutarate, etc). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid (DMPS). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of p- aminohippurate (PAH), ochratoxin (OTA), acyclovir (ACV), 3'-azido- 3-'deoxythymidine (AZT), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro- phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), hippurate (HA), indoleacetate (IA), indoxyl sulfate (IS) and 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2- furanpropionate (CMPF), cidofovir, adefovir, 9-(2- phosphonylmethoxyethyl) guanine (PMEG), 9-(2- phosphonylmethoxyethyl) diaminopurine (PMEDAP) and edaravone sulfate. PAH uptake is inhibited by p- chloromercuribenzenesulphonate (PCMBS), diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), sulindac, diclofenac, carprofen, glutarate and okadaic acid. PAH uptake is inhibited by benzothiazolylcysteine (BTC), S-chlorotrifluoroethylcysteine (CTFC), cysteine S-conjugates S-dichlorovinylcysteine (DCVC), furosemide, steviol, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), calcium ionophore A23187, benzylpenicillin, furosemide, indomethacin, bumetamide, losartan, probenecid, phenol red, urate, and alpha-ketoglutarate
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q4U2R8
- Molecular weight:
- 61815.8
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 1085 proteins in total.