| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-08-16 13:52:05 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:09 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001362 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydrogen |
|---|
| Description | Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, nonmetallic, tasteless, highly flammable diatomic gas with the molecular formula H2. With an atomic weight of 1.00794, hydrogen is the lightest element. Besides the common H1 isotope, hydrogen exists as the stable isotope Deuterium and the unstable, radioactive isotope Tritium. Hydrogen is the most abundant of the chemical elements, constituting roughly 75% of the universe's elemental mass. Hydrogen can form compounds with most elements and is present in water and most organic compounds. It plays a particularly important role in acid-base chemistry, in which many reactions involve the exchange of protons between soluble molecules. Oxidation of hydrogen, in the sense of removing its electron, formally gives H+, containing no electrons and a nucleus which is usually composed of one proton. That is why H+ is often called a proton. This species is central to discussion of acids. Under the Bronsted-Lowry theory, acids are proton donors, while bases are proton acceptors. A bare proton H+ cannot exist in solution because of its strong tendency to attach itself to atoms or molecules with electrons. However, the term 'proton' is used loosely to refer to positively charged or cationic hydrogen, denoted H+. H2 is a product of some types of anaerobic metabolism and is produced by several microorganisms, usually via reactions catalyzed by iron- or nickel-containing enzymes called hydrogenases. These enzymes catalyze the reversible redox reaction between H2 and its component two protons and two electrons. Creation of hydrogen gas occurs in the transfer of reducing equivalents produced during pyruvate fermentation to water. Hydrogen has been found to be a metabolite of Citrobacter, Cyanobacteria, Enterobacter, Halobacterium and Rhodobacteraceae (PMID: 28042989 ; PMID: 16371161 ) (https://www.insa.nic.in/writereaddata/UpLoadedFiles/PINSA/Vol51B_1985_2_Art16.pdf) (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222428793_High_Hydrogen_Yield_from_a_Two-step_Process_of_Dark-_and_Photo-fermentation_of_Sucrose) (Tao, Y; Chen, Y; Wu, Y; He, Y; Zhou, Z (2007). "High hydrogen yield from a two-step process of dark- and photo-fermentation of sucrose". International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 32 (2): 200-206). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| e 949 | ChEBI | | e-949 | ChEBI | | e949 | ChEBI | | H2 | ChEBI | | Molecular hydrogen | ChEBI | | Dihydrogen | HMDB | | Hydrogen gas | HMDB | | Hydrogen-1 | MeSH, HMDB | | Hydrogen 1 | MeSH, HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | H2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 2.0159 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 2.015650064 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | dihydrogen |
|---|
| Traditional Name | dihydrogen |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 1333-74-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][H] |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/H2/h1H |
|---|
| InChI Key | UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as other non-metal hydrides. These are inorganic compounds in which the heaviest atom bonded to a hydrogen atom is belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Class | Other non-metal organides |
|---|
| Sub Class | Other non-metal hydrides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Other non-metal hydrides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | Not Available |
|---|
| Substituents | |
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Not Available | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | -259.2 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | -252.77 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg (est) | The Good Scents Company Information System | | Water Solubility | 0.0016 mg/mL at 21 °C | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections| Predictor | Adduct Type | CCS Value (Å2) | Reference |
|---|
| DeepCCS | [M+H]+ | 110.643 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M-H]- | 108.835 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M-2H]- | 144.009 | 30932474 | | DeepCCS | [M+Na]+ | 117.588 | 30932474 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hydrogen 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9000000000-0595c445077141efd7ac | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hydrogen 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9000000000-0595c445077141efd7ac | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hydrogen 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9000000000-0595c445077141efd7ac | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hydrogen 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9000000000-cbcf030cfea82ec88da3 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hydrogen 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9000000000-cbcf030cfea82ec88da3 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Hydrogen 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9000000000-cbcf030cfea82ec88da3 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Peroxisome
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
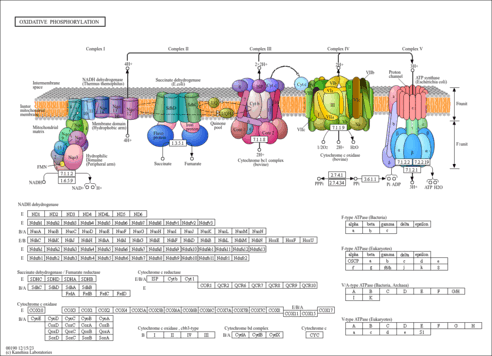
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB016247 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00023091 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 762 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00282 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | HYDROGEN-MOLECULE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33778 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Hydrogen |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 783 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 18276 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | H2 |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | rw1250851 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Ait-Ichou, I.; Formenti, M.; Pommier, B.; Teichner, S. J. Photocatalytic dehydrogenation of isopropanol on platinum/titania catalysts. Journal of Catalysis (1985), 91(2), 293-307. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Asadi N, Zilouei H: Optimization of organosolv pretreatment of rice straw for enhanced biohydrogen production using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol. 2017 Mar;227:335-344. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.073. Epub 2016 Dec 23. [PubMed:28042989 ]
- Dutta D, De D, Chaudhuri S, Bhattacharya SK: Hydrogen production by Cyanobacteria. Microb Cell Fact. 2005 Dec 21;4:36. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-4-36. [PubMed:16371161 ]
|
|---|