| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-08-12 19:22:48 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:16:38 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003364 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Quinone |
|---|
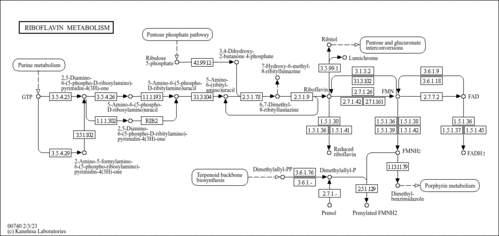
| Description | Quinone is also called 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione. Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds and are often readily made from reactive aromatic compounds with electron-donating substituents such as phenols and catechols, which increase the nucleophilicity of the ring and contributes to the large redox potential needed to break aromaticity. Derivatives of quinones are common constituents of biologically relevant molecules. Some serve as electron acceptors in electron transport chains such as those in photosynthesis (plastoquinone, phylloquinone), and aerobic respiration (ubiquinone). Quinone is a common constituent of biologically relevant molecules (e.g. Vitamin K1 is phylloquinone). A natural example of quinones as oxidizing agents is the spray of bombardier beetles. Hydroquinone is reacted with hydrogen peroxide to produce a fiery blast of steam, a strong deterent in the animal world. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C6H4O2/c7-5-1-2-6(8)4-3-5/h1-4H |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 1,4-Benzochinon | ChEBI | | 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione | ChEBI | | Benzo-1,4-quinone | ChEBI | | Benzoquinone | ChEBI | | p-Benzoquinone | ChEBI | | p-Chinon | ChEBI | | p-Quinone | ChEBI | | Para-benzoquinone | ChEBI | | Chinone | Kegg | | 1,4-Benzoquinone | Kegg | | 1,4-Benzoquine | HMDB | | 1,4-Cyclohexadiene dioxide | HMDB | | 1,4-Cyclohexadienedione | HMDB | | 1,4-Diossibenzene | HMDB | | 1,4-Dioxy-benzol | HMDB | | 1,4-Dioxybenzene | HMDB | | 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1-4-dione | HMDB | | Benzo-chinon | HMDB | | Chinon | HMDB | | Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione | HMDB | | Cyclohexadienedione | HMDB | | Eldoquin | HMDB | | Para-quinone | HMDB | | Quinone1,4-benzoquinone | HMDB | | Semiquinone anion | HMDB | | Semiquinone radicals | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H4O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 108.0948 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 108.021129372 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione |
|---|
| Traditional Name | quinone |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 106-51-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | O=C1C=CC(=O)C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H4O2/c7-5-1-2-6(8)4-3-5/h1-4H |
|---|
| InChI Key | AZQWKYJCGOJGHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as p-benzoquinones. These are benzoquinones where the two C=O groups are attached at the 1- and 4-positions, respectively. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbonyl compounds |
|---|
| Direct Parent | P-benzoquinones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - P-benzoquinone
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 115.7 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 11.1 mg/mL at 18 °C | Not Available | | LogP | 0.20 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 3.25 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 9.3827 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 1.62 minutes | 32390414 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1071.0 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 362.7 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 111.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 259.0 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 74.4 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 303.8 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 371.2 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 260.5 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 756.2 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 221.0 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 888.1 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 267.8 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 239.9 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 555.4 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 336.6 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 119.0 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized |
|---|
| General References | - Kwasnicka-Crawford DA, Vincent SR: Role of a novel dual flavin reductase (NR1) and an associated histidine triad protein (DCS-1) in menadione-induced cytotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Oct 21;336(2):565-71. [PubMed:16140270 ]
- Fabiani R, De Bartolomeo A, Morozzi G: Involvement of oxygen free radicals in the serum-mediated increase of benzoquinone genotoxicity. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2005 Oct;46(3):156-63. [PubMed:15920754 ]
- Gaskell M, McLuckie KI, Farmer PB: Comparison of the repair of DNA damage induced by the benzene metabolites hydroquinone and p-benzoquinone: a role for hydroquinone in benzene genotoxicity. Carcinogenesis. 2005 Mar;26(3):673-80. Epub 2004 Dec 23. [PubMed:15618234 ]
- Bello RI, Gomez-Diaz C, Navarro F, Alcain FJ, Villalba JM: Expression of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 in HeLa cells: role of hydrogen peroxide and growth phase. J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 30;276(48):44379-84. Epub 2001 Sep 20. [PubMed:11567026 ]
- Park S, Geddes TJ, Javitch JA, Kuhn DM: Dopamine prevents nitration of tyrosine hydroxylase by peroxynitrite and nitrogen dioxide: is nitrotyrosine formation an early step in dopamine neuronal damage? J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 1;278(31):28736-42. Epub 2003 May 27. [PubMed:12771134 ]
- Siegel D, Ryder J, Ross D: NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 expression in human bone marrow endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 2001 Dec 15;125(1-3):93-8. [PubMed:11701227 ]
- Roberg K, Johansson U, Ollinger K: Lysosomal release of cathepsin D precedes relocation of cytochrome c and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential during apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999 Dec;27(11-12):1228-37. [PubMed:10641715 ]
- Yamazaki H, Shibata A, Suzuki M, Nakajima M, Shimada N, Guengerich FP, Yokoi T: Oxidation of troglitazone to a quinone-type metabolite catalyzed by cytochrome P-450 2C8 and P-450 3A4 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999 Nov;27(11):1260-6. [PubMed:10534310 ]
- He K, Woolf TF, Kindt EK, Fielder AE, Talaat RE: Troglitazone quinone formation catalyzed by human and rat CYP3A: an atypical CYP oxidation reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001 Jul 15;62(2):191-8. [PubMed:11389877 ]
- Soucek P: Cytochrome P450 destruction by quinones: comparison of effects in rat and human liver microsomes. Chem Biol Interact. 1999 Aug 1;121(3):223-36. [PubMed:10462055 ]
- Xu L, Eiseman JL, Egorin MJ, D'Argenio DZ: Physiologically-based pharmacokinetics and molecular pharmacodynamics of 17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin and its active metabolite in tumor-bearing mice. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2003 Jun;30(3):185-219. [PubMed:14571691 ]
- He K, Talaat RE, Woolf TF: Incorporation of an oxygen from water into troglitazone quinone by cytochrome P450 and myeloperoxidase. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004 Apr;32(4):442-6. [PubMed:15039298 ]
- Toyota T, Ueno Y: [Clinical effect and side effect of troglitazone]. Nihon Rinsho. 2000 Feb;58(2):376-82. [PubMed:10707561 ]
- Smith MT: The mechanism of benzene-induced leukemia: a hypothesis and speculations on the causes of leukemia. Environ Health Perspect. 1996 Dec;104 Suppl 6:1219-25. [PubMed:9118896 ]
- Terman A, Neuzil J, Kagedal K, Ollinger K, Brunk UT: Decreased apoptotic response of inclusion-cell disease fibroblasts: a consequence of lysosomal enzyme missorting? Exp Cell Res. 2002 Mar 10;274(1):9-15. [PubMed:11855852 ]
- Mu D, Medzihradszky KF, Adams GW, Mayer P, Hines WM, Burlingame AL, Smith AJ, Cai D, Klinman JP: Primary structures for a mammalian cellular and serum copper amine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9926-32. [PubMed:8144587 ]
- Hasegawa T, Matsuzaki M, Takeda A, Kikuchi A, Furukawa K, Shibahara S, Itoyama Y: Increased dopamine and its metabolites in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells that express tyrosinase. J Neurochem. 2003 Oct;87(2):470-5. [PubMed:14511124 ]
|
|---|