| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 14:17:31 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:12 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0002009 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0059627
- HMDB02009
- HMDB59627
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Crotonoyl-CoA |
|---|
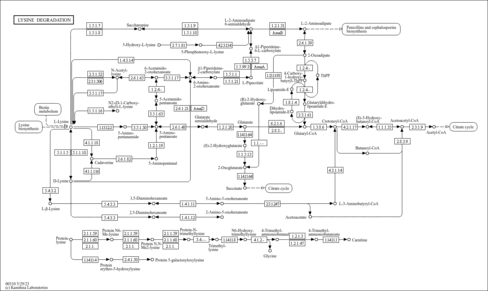
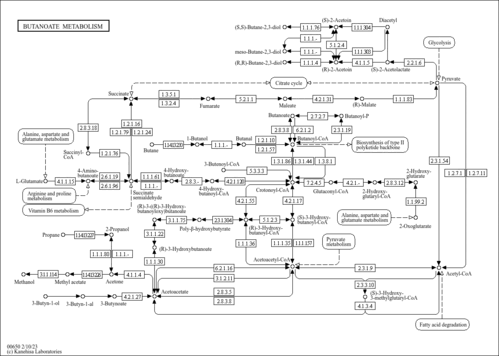
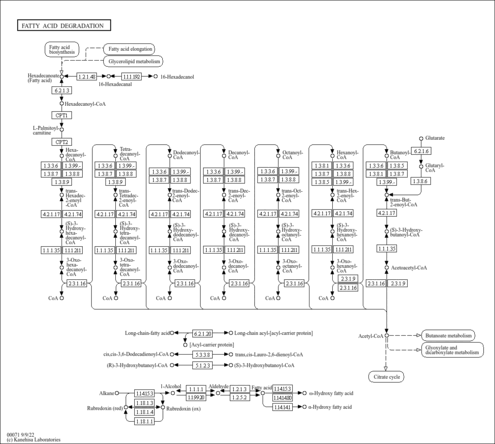
| Description | Crotonoyl-CoA (CAS: 992-67-6) is an important component in several metabolic pathways, notably fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is the substrate of acyl-coenzyme A oxidases 1, 2, and 3 (EC 1.3.3.6) corresponding to palmitoyl, branched-chain, and pristanoyl, respectively. In peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation, these enzymes produce hydrogen peroxide. Abnormalities in this group of enzymes are linked to coma, dehydration, diabetes, fatty liver, hyperinsulinemia, hyperlipidemia, and leukodystrophy. Crotonoyl-CoA is also a substrate of a group of enzymes called acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenases (EC 1.3.99-, 1.3.99.2, 1.3.99.3) in the metabolism of fatty acids or branched-chain amino acids in the mitochondria (PMID: 7698750 ). Acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase has been shown to contribute to kidney-associated diseases, such as adrenogential syndrome, kidney failure, kidney tubular necrosis, homocystinuria, as well as other diseases including cretinism, encephalopathy, hypoglycemia, and medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. The gene (ACADS) also plays a role in theta oscillation during sleep. In addition, crotonoyl-CoA is the substrate of enoyl-coenzyme A hydratase (EC 4.2.1.17) in the mitochondria during lysine degradation and tryptophan metabolism as well as benzoate degradation via CoA ligation. Crotonoyl-CoA is the product of this enzyme in butanoate metabolism. Moreover, it is produced from multiple enzymes in the butanoate metabolism pathway, including 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.55), glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.70), vinylacetyl-CoA delta-isomerase (EC 5.3.3.3), and trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase (NAD+) (EC 1.3.1.44). In lysine degradation and tryptophan metabolism, crotonoyl-CoA is produced by glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.7). This enzyme is linked to glutaric aciduria type I, metabolic diseases, movement disorders, myelinopathy, and nervous system diseases. |
|---|
| Structure | [H]\C(C)=C(\[H])C(=O)SCCN=C(O)CCN=C(O)[C@]([H])(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@@]1([H])O[C@@]([H])(N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C23)[C@]([H])(O)[C@]1([H])OP(O)(O)=O InChI=1S/C25H40N7O17P3S/c1-4-5-16(34)53-9-8-27-15(33)6-7-28-23(37)20(36)25(2,3)11-46-52(43,44)49-51(41,42)45-10-14-19(48-50(38,39)40)18(35)24(47-14)32-13-31-17-21(26)29-12-30-22(17)32/h4-5,12-14,18-20,24,35-36H,6-11H2,1-3H3,(H,27,33)(H,28,37)(H,41,42)(H,43,44)(H2,26,29,30)(H2,38,39,40)/b5-4+/t14-,18-,19-,20+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Crotonyl-CoA | ChEBI | | trans-But-2-enoyl-CoA | ChEBI | | trans-Butyr-2-enoyl-CoA | ChEBI | | 2-Butenoyl-CoA | Kegg | | But-2-enoyl-CoA | Kegg | | (2E)-But-2-enoyl-CoA | Kegg | | Crotonyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | (e)-But-2-enoyl-CoA | ChEBI | | Crotonoyl-CoA | HMDB | | Crotonoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | Crotonyl coenzyme A | HMDB | | trans-2-Butenoyl-CoA | HMDB | | trans-2-Butenoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | trans-Crotonoyl-CoA | HMDB | | trans-Crotonoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | trans-Crotonyl CoA | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C25H40N7O17P3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 835.608 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 835.141423115 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-4-({[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-N-[2-({2-[(2E)-but-2-enoylsulfanyl]ethyl}-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)ethyl]-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanimidic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2R)-4-[({[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]-N-[2-({2-[(2E)-but-2-enoylsulfanyl]ethyl}-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)ethyl]-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanimidic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 38795-21-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | C\C=C\C(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)[C@H](O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C25H40N7O17P3S/c1-4-5-16(34)53-9-8-27-15(33)6-7-28-23(37)20(36)25(2,3)11-46-52(43,44)49-51(41,42)45-10-14-19(48-50(38,39)40)18(35)24(47-14)32-13-31-17-21(26)29-12-30-22(17)32/h4-5,12-14,18-20,24,35-36H,6-11H2,1-3H3,(H,27,33)(H,28,37)(H,41,42)(H,43,44)(H2,26,29,30)(H2,38,39,40)/b5-4+/t14-,18-,19-,20+,24-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KFWWCMJSYSSPSK-PAXLJYGASA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2-enoyl coas. These are organic compounds containing a coenzyme A substructure linked to a 2-enoyl chain. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 2-enoyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- 6-aminopurine
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Aminopyrimidine
- Imidolactam
- N-acyl-amine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Monosaccharide
- Pyrimidine
- Alkyl phosphate
- Fatty amide
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Sulfenyl compound
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Oxacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organosulfur compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Amine
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 3.53 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 10.3137 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 9.25 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 516.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Long = Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 1270.2 seconds | 40023050 | | Fem_Lipids = Ascentis Express C18 with (60:40 water:ACN):(90:10 IPA:ACN) and 10mM NH4COOH + 0.1% Formic Acid | 169.8 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_Old = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:(20:80 acetone:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 94.1 seconds | 40023050 | | Life_New = RP Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18 with Water:(30:70 MeOH:ACN) and 0.1% Formic Acid | 162.8 seconds | 40023050 | | RIKEN = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 77.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Eawag_XBridgeC18 = XBridge C18 3.5u 2.1x50 mm with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 365.0 seconds | 40023050 | | BfG_NTS_RP1 =Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm x 150 mm, 3.5 um) with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 422.0 seconds | 40023050 | | HILIC_BDD_2 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN(0.1% formic acid):water(16 mM ammonium formate) | 822.4 seconds | 40023050 | | UniToyama_Atlantis = RP Waters Atlantis T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 um) with ACN:Water and 0.1% Formic Acid | 664.2 seconds | 40023050 | | BDD_C18 = Hypersil Gold 1.9µm C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 302.1 seconds | 40023050 | | UFZ_Phenomenex = Kinetex Core-Shell C18 2.6 um, 3.0 x 100 mm, Phenomenex with Water:MeOH and 0.1% Formic Acid | 677.7 seconds | 40023050 | | SNU_RIKEN_POS = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 225.7 seconds | 40023050 | | RPMMFDA = Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 with Water:ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | 224.4 seconds | 40023050 | | MTBLS87 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water and :ammonium carbonate | 470.7 seconds | 40023050 | | KI_GIAR_zic_HILIC_pH2_7 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-HILIC with ACN:Water and 0.1% FA | 358.5 seconds | 40023050 | | Meister zic-pHILIC pH9.3 = Merck SeQuant ZIC-pHILIC column with ACN:Water 5mM NH4Ac pH9.3 and 5mM ammonium acetate in water | 331.6 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized |
|---|
| MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kr-1921000110-de694ebfa0837735d1be | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000l-1911000000-5b106b3a07df5c8c3755 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1920000000-2ecd1925643a7cc3e17f | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00lr-7920142560-10f7deae9d59f3fd3b6d | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-6910110000-fc85ca4055cec31805dc | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-057i-5900100000-a22910037b80042e1f67 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-053r-0000000090-ab823464181bc32f03d2 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-9100102220-fd6f03390bd7a43d01c1 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0170-5003512900-74bcb83a0ff12e7c4a9b | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0000000190-99bf5276fb1e28f0a070 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0901002270-22f1df5d925d91d4db45 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Crotonoyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0219000000-59474207fbf5193eca0d | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| General References | - Fu Z, Wang M, Paschke R, Rao KS, Frerman FE, Kim JJ: Crystal structures of human glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase with and without an alternate substrate: structural bases of dehydrogenation and decarboxylation reactions. Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 3;43(30):9674-84. [PubMed:15274622 ]
- Rozen R, Vockley J, Zhou L, Milos R, Willard J, Fu K, Vicanek C, Low-Nang L, Torban E, Fournier B: Isolation and expression of a cDNA encoding the precursor for a novel member (ACADSB) of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene family. Genomics. 1994 Nov 15;24(2):280-7. [PubMed:7698750 ]
- Hyman DB, Tanaka K: Specific glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenating activity is deficient in cultured fibroblasts from glutaric aciduria patients. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):778-84. [PubMed:6423663 ]
- Kalousek F, Darigo MD, Rosenberg LE: Isolation and characterization of propionyl-CoA carboxylase from normal human liver. Evidence for a protomeric tetramer of nonidentical subunits. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):60-5. [PubMed:6765947 ]
- Dwyer TM, Rao KS, Westover JB, Kim JJ, Frerman FE: The function of Arg-94 in the oxidation and decarboxylation of glutaryl-CoA by human glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 5;276(1):133-8. [PubMed:11024031 ]
- Babidge W, Millard S, Roediger W: Sulfides impair short chain fatty acid beta-oxidation at acyl-CoA dehydrogenase level in colonocytes: implications for ulcerative colitis. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998 Apr;181(1-2):117-24. [PubMed:9562248 ]
- Lenich AC, Goodman SI: The purification and characterization of glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase from porcine and human liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4090-6. [PubMed:3081514 ]
- Gregersen N, Brandt NJ, Christensen E, Gron I, Rasmussen K, Brandt S: Glutaric aciduria: clinical and laboratory findings in two brothers. J Pediatr. 1977 May;90(5):740-5. [PubMed:853337 ]
- Hodgins MB: Possible mechanisms of androgen resistance in 5 alpha-reductase deficiency: implications for the physiological roles of 5 alpha-reductases. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1B):555-9. [PubMed:6887883 ]
- Saenger AK, Nguyen TV, Vockley J, Stankovich MT: Thermodynamic regulation of human short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by substrate and product binding. Biochemistry. 2005 Dec 13;44(49):16043-53. [PubMed:16331964 ]
- Finocchiaro G, Ito M, Tanaka K: Purification and properties of short chain acyl-CoA, medium chain acyl-CoA, and isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenases from human liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7982-9. [PubMed:3597357 ]
- Simons K, Toomre D: Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):31-9. [PubMed:11413487 ]
- Watson AD: Thematic review series: systems biology approaches to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Lipidomics: a global approach to lipid analysis in biological systems. J Lipid Res. 2006 Oct;47(10):2101-11. Epub 2006 Aug 10. [PubMed:16902246 ]
- Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ: Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res. 2007 Jun;48(6):1253-62. Epub 2007 Mar 20. [PubMed:17374880 ]
- Lingwood D, Simons K: Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science. 2010 Jan 1;327(5961):46-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. [PubMed:20044567 ]
- Gunstone, Frank D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra (2007). The lipid handbook with CD-ROM. CRC Press.
|
|---|