| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:14:38 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000227 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB00227
- HMDB0059629
- HMDB59629
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Mevalonic acid |
|---|
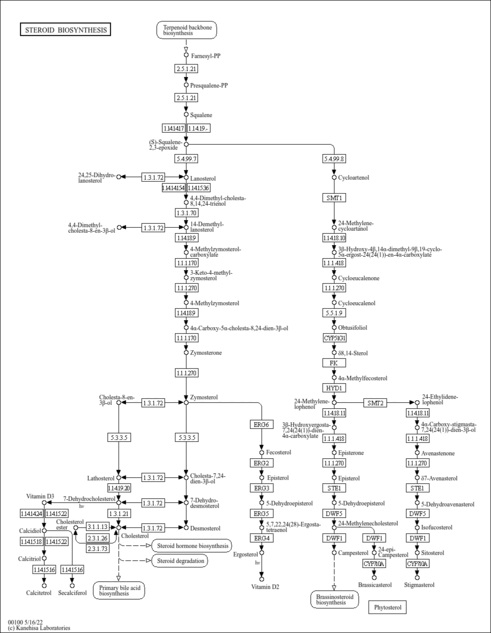
| Description | Mevalonic acid, also known as MVA, mevalonate, or hiochic acid, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxy fatty acids. These are fatty acids in which the chain bears a hydroxyl group. Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. It is found in most higher organisms ranging from plants to animals. Mevalonic acid is a precursor in the biosynthetic pathway known as the mevalonate pathway that produces terpenes (in plants) and steroids (in animals). Mevalonic acid is the primary precursor of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), that is in turn the basis for all terpenoids. The production of mevalonic acid by the enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, is the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol (PMID: 12872277 ). The cholesterol biosynthetic pathway has three major steps: (1) acetate to mevalonate, (2) mevalonate to squalene, and (3) squalene to cholesterol. In the first step, which catalyzed by thiolase, two acetyl-CoA molecules form acetoacetyl-CoA and one CoA molecule is released, then the acetoacetyl-CoA reacts with another molecule of acetyl-CoA and generates 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMGCoA). The enzyme responsible for this reaction is 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMG-CoA synthase): In the pathway to synthesize cholesterol, one of the HMG-CoA carboxyl groups undergoes reduction to an alcohol, releasing CoA, leading to the formation of mevalonate, a six carbon compound. This reaction is catalyzed by hydroxy-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, In the second step (mevalonate to squalene) mevalonate receives a phosphoryl group from ATP to form 5-phosphomevalonate. This compound accepts another phosphate to generate mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate. After a third phosphorylation, the compound is decarboxylated, loses water, and generates isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP). Then through successive condensations, IPP forms squalene, a terpene hydrocarbon that contains 30 carbon atoms. By cyclization and other changes, this compound will finally result in cholesterol. Mevalonic acid is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as apples, corns, and wild carrots and in a lower concentration in garden tomato (var.), pepper (C. frutescens), and cucumbers. Mevalonic acid has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as sweet oranges, potato, milk (cow), cabbages, and white cabbages. This could make mevalonic acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of MVA are decreased by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drugs such as pravastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin (PMID: 8808497 ). |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C6H12O4/c1-6(10,2-3-7)4-5(8)9/h7,10H,2-4H2,1H3,(H,8,9)/t6-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (R)-3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylvaleric acid | ChEBI | | (R)-Mevalonate | ChEBI | | 3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylvaleric acid | ChEBI | | (R)-3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylvalerate | Generator | | (R)-Mevalonic acid | Generator | | 3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylvalerate | Generator | | Mevalonate | Generator | | Mevalonic acid | ChEBI | | Acid, mevalonic | MeSH | | (3R)-3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid | HMDB | | (3R)-Mevalonic acid | HMDB | | (R)-(-)-Mevalonic acid | HMDB | | (R)-3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid | HMDB | | 2,4-Dideoxy-3-C-methylpentonic acid | HMDB | | 3,5-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid | HMDB | | Hiochic acid | HMDB | | MVA | HMDB | | R-Mevalonic acid | HMDB | | beta,delta-Dihydroxy-beta-methylvaleric acid | HMDB | | β,δ-Dihydroxy-β-methylvaleric acid | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H12O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 148.1571 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 148.073558872 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (3R)-3,5-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | mevalonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 17817-88-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[C@@](O)(CCO)CC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H12O4/c1-6(10,2-3-7)4-5(8)9/h7,10H,2-4H2,1H3,(H,8,9)/t6-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KJTLQQUUPVSXIM-ZCFIWIBFSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxy fatty acids. These are fatty acids in which the chain bears a hydroxyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acids and conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Hydroxy fatty acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Branched fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Short-chain hydroxy acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Tertiary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Organooxygen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 24 - 27 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Retention Times Underivatized| Chromatographic Method | Retention Time | Reference |
|---|
| Measured using a Waters Acquity ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm; 1.7 μmparticle diameter). Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. Predicted by Afia on May 17, 2022. | 1.81 minutes | 32390414 | | Predicted by Siyang on May 30, 2022 | 9.2249 minutes | 33406817 | | Predicted by Siyang using ReTip algorithm on June 8, 2022 | 5.0 minutes | 32390414 | | AjsUoB = Accucore 150 Amide HILIC with 10mM Ammonium Formate, 0.1% Formic Acid | 190.4 seconds | 40023050 |
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1427.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1301.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1918.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@](O)(CCO[Si](C)(C)C)CC(=O)O | 1425.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@](O)(CCO[Si](C)(C)C)CC(=O)O | 1323.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@](O)(CCO[Si](C)(C)C)CC(=O)O | 1919.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@](O)(CCO)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1386.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@](O)(CCO)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1324.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@](O)(CCO)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1909.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO[Si](C)(C)C)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1532.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO[Si](C)(C)C)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1448.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO[Si](C)(C)C)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1667.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@](CCO)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1467.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@](CCO)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1460.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@](CCO)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1658.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@](O)(CCO[Si](C)(C)C)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1474.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@](O)(CCO[Si](C)(C)C)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1475.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@](O)(CCO[Si](C)(C)C)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1672.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO[Si](C)(C)C)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1556.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO[Si](C)(C)C)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1567.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@](CCO[Si](C)(C)C)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1497.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@](C)(CCO)CC(=O)O | 1662.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@](C)(CCO)CC(=O)O | 1502.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@](C)(CCO)CC(=O)O | 1958.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@@](C)(O)CC(=O)O | 1660.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@@](C)(O)CC(=O)O | 1517.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@@](C)(O)CC(=O)O | 2021.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)C[C@](C)(O)CCO | 1613.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)C[C@](C)(O)CCO | 1521.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)C[C@](C)(O)CCO | 1985.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@](C)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1977.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@](C)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1865.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@](C)(CC(=O)O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1903.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)C[C@@](C)(CCO)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1912.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)C[C@@](C)(CCO)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1900.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)C[C@@](C)(CCO)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1883.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@@](C)(O)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1911.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@@](C)(O)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1889.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@@](C)(O)CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1916.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@](C)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2208.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@](C)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2159.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Mevalonic acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OCC[C@](C)(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1917.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
|
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0f79-9400000000-1432953ab200e13ed3a7 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00bj-9372000000-2a6b263d37306947c327 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0002-2900000000-d1dc97020c103f2a916b | 2020-04-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-014i-9000000000-b4dc45e964aee6759d93 | 2020-04-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-014i-9100000000-98f7e8ee013680f4f610 | 2020-04-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01q9-2900000000-00a30c20b0fe2afce7d8 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03ej-9700000000-c6f9687555150d5ef1a7 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01bi-9100000000-7047d67f0ba1f8aa28ef | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0f72-3900000000-0f765b34011b73405add | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-9500000000-dd24fe04989af5af1151 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052s-9100000000-251b958b3e4355c6f2f6 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0fbj-2900000000-fb0c642b03cb9422a9e4 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4r-9300000000-1b45622114c4f19f4a9a | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-42ee087c307b5e92b059 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01qa-3900000000-2c25572adb2588760845 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000j-9200000000-b6d834223509e1430e61 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Mevalonic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-e4b7f6f9a91f771bd453 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2020-04-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2020-04-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Endoplasmic reticulum
- Peroxisome
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Fibroblasts
- Leukocyte
- Liver
|
|---|
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.043 +/- 0.013 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.028 +/- 0.006 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.026(0.013-0.042) uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.5 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.0531 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.178 (0.0515-0.545) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.14 (0.06-0.22) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.160 (0.0800-0.300) umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.012 +/- 0.002 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 70-540 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Mevalonic aciduria | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 20-140 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Mevalonic aciduria | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Attachment loss | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Missing teeth | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Periodontal Probing Depth | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Tooth Decay | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2100-56000 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Mevalonic aciduria | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 900-14500 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Mevalonic aciduria | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome |
|---|
- Honda M, Tint GS, Honda A, Salen G, Shefer S, Batta AK, Matsuzaki Y, Tanaka N: Regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in patients with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2000 Jul;23(5):464-74. [PubMed:10947201 ]
| | Attachment loss |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Missing teeth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Periodontal Probing Depth |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Tooth Decay |
|---|
- Liebsch C, Pitchika V, Pink C, Samietz S, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Suhre K, Adamski J, Nauck M, Volzke H, Friedrich N, Kocher T, Holtfreter B, Pietzner M: The Saliva Metabolome in Association to Oral Health Status. J Dent Res. 2019 Jun;98(6):642-651. doi: 10.1177/0022034519842853. Epub 2019 Apr 26. [PubMed:31026179 ]
| | Mevalonic aciduria |
|---|
- Hoffmann GF, Charpentier C, Mayatepek E, Mancini J, Leichsenring M, Gibson KM, Divry P, Hrebicek M, Lehnert W, Sartor K, et al.: Clinical and biochemical phenotype in 11 patients with mevalonic aciduria. Pediatrics. 1993 May;91(5):915-21. [PubMed:8386351 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 270400 (Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome)
- 610377 (Mevalonic aciduria)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB03518 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB005126 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001195 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 388367 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00418 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | MEVALONATE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Mevalonic_acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 439230 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17710 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | MEV_R |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000109 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Takahara, Kenji; Nakamura, Yoshio; Ohashi, Takehisa; Watanabe, Kiyoshi. Fermentative production of mevalonic acid. Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho (1985), 4 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Houten SM, Kuis W, Duran M, de Koning TJ, van Royen-Kerkhof A, Romeijn GJ, Frenkel J, Dorland L, de Barse MM, Huijbers WA, Rijkers GT, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ, Poll-The BT: Mutations in MVK, encoding mevalonate kinase, cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome. Nat Genet. 1999 Jun;22(2):175-7. [PubMed:10369261 ]
- Hoffmann G, Gibson KM, Brandt IK, Bader PI, Wappner RS, Sweetman L: Mevalonic aciduria--an inborn error of cholesterol and nonsterol isoprene biosynthesis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 19;314(25):1610-4. [PubMed:3012338 ]
- Dmitrieva NA, Perrun'kina AM, Khomulo PS: [Determination of mevalonic acid in the urine and its concentration in the urine of patients with atherosclerosis]. Vopr Med Khim. 1968 Jan-Feb;14(1):106-8. [PubMed:5683362 ]
- Larson RA, Chung J, Scanu AM, Yachnin S: Neutrophils are required for the DNA synthetic response of human lymphocytes to mevalonic acid: evidence suggesting that a nonsterol product of mevalonate is involved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3028-32. [PubMed:6953445 ]
- Siavoshian S, Simoneau C, Maugeais P, Marks L, Rodary L, Gardette J, Krempf M: Measurement of mevalonic acid in human urine by bench top gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 1995 Dec 29;243(2):129-36. [PubMed:8747489 ]
- Mitchell ED Jr, Avigan J: Control of phosphorylation and decarboxylation of mevalonic acid and its metabolites in cultured human fibroblasts and in rat liver in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6170-3. [PubMed:6263908 ]
- Abrar M, Martin PD: Validation and application of an assay for the determination of mevalonic acid in human plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002 Jun 25;773(2):103-11. [PubMed:12031835 ]
- Haas D, Kelley RI, Hoffmann GF: Inherited disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis. Neuropediatrics. 2001 Jun;32(3):113-22. [PubMed:11521206 ]
- Larson RA, Kluskens LE, Yachnin S: The DNA synthetic response of normal and abnormal human lymphocytes to mevalonic acid: the role of granulocytes as a helper population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Sep;74(3 Pt 1):280-90. [PubMed:6236250 ]
- Larson RA, Yachnin S: Mevalonic acid induces DNA synthesis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):257-62. [PubMed:6610447 ]
- Parker TS, McNamara DJ, Brown CD, Kolb R, Ahrens EH Jr, Alberts AW, Tobert J, Chen J, De Schepper PJ: Plasma mevalonate as a measure of cholesterol synthesis in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):795-804. [PubMed:6565710 ]
- Hoffmann GF, Sweetman L, Bremer HJ, Hunneman DH, Hyanek J, Kozich V, Lehnert W, Nyhan WL, Speidel I, Trefz FK, et al.: Facts and artefacts in mevalonic aciduria: development of a stable isotope dilution GCMS assay for mevalonic acid and its application to physiological fluids, tissue samples, prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 May 15;198(3):209-27. [PubMed:1653652 ]
- Jemal M, Schuster A, Whigan DB: Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry methods for quantitation of mevalonic acid in human plasma and urine: method validation, demonstration of using a surrogate analyte, and demonstration of unacceptable matrix effect in spite of use of a stable isotope analog internal standard. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003;17(15):1723-34. [PubMed:12872277 ]
- Lindenthal B, von Bergmann K: Urinary excretion and serum concentration of mevalonic acid during acute intake of alcohol. Metabolism. 2000 Jan;49(1):62-6. [PubMed:10647065 ]
- Simons K, Toomre D: Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):31-9. [PubMed:11413487 ]
- Watson AD: Thematic review series: systems biology approaches to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Lipidomics: a global approach to lipid analysis in biological systems. J Lipid Res. 2006 Oct;47(10):2101-11. Epub 2006 Aug 10. [PubMed:16902246 ]
- Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ: Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res. 2007 Jun;48(6):1253-62. Epub 2007 Mar 20. [PubMed:17374880 ]
- Lingwood D, Simons K: Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science. 2010 Jan 1;327(5961):46-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. [PubMed:20044567 ]
- Naoumova RP, Marais AD, Mountney J, Firth JC, Rendell NB, Taylor GW, Thompson GR: Plasma mevalonic acid, an index of cholesterol synthesis in vivo, and responsiveness to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Atherosclerosis. 1996 Jan 26;119(2):203-13. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(95)05649-1. [PubMed:8808497 ]
- Gunstone, Frank D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra (2007). The lipid handbook with CD-ROM. CRC Press.
|
|---|